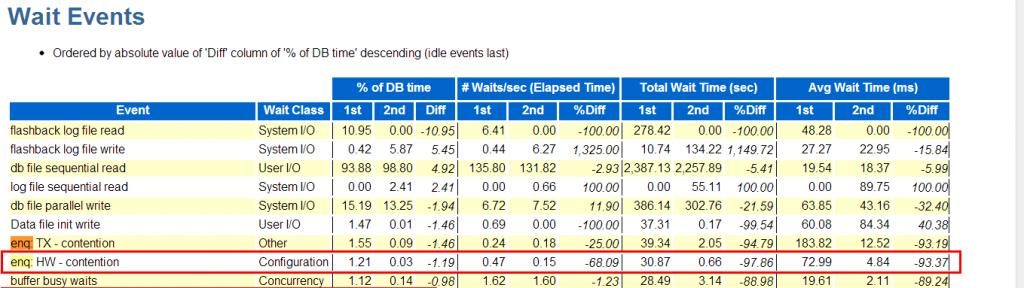
IV,Library Cache Invalidation Enqueue Lock
相关资源:
在Library cache中当前被缓存的有效或已存数据库对象,例如 表TABLE、视图View、存储过程procedure、package、package body、trigger、index、cluster、synonym;或cursor (SQL or PL/SQL)、pipe、等多种多样的库缓存资源类型
相关用户:
所有的可能的Oracle前台或后台进程
锁的原因:
LCK后台进程及其他进程视图在集群中的所有实例上使相关的library cache object失效(invalidate)
何时使用该队列锁?
当一个有效或现存的数据库对象被加载到library cache库缓存中,LCK RAC后台进程将针对该resource要求一个S共享模式的IV队列锁。直到该对象或者失效或者不再存在或者被age out出library cache,该IV lock才会被释放。 该IV lock存在的目的是在所有实例间使library cache中缓存的对象失效。 若一个进程想要使library cache object失效则首先请求以X mode锁定该对象资源,这将导致所有实例中均使该缓存对象失效以响应BAST并释放他们在该对象上的IV lock,之后发起invalidate进程将释放该X lock。
ID1、ID2的组合:
Object Number, Timestamp
Lock Value Block:
Not Used.
Init.ora Parameters:
None.
Scope:
Global Lock.
Deadlock Sensitive:
No.
Operation:
Synchronous.